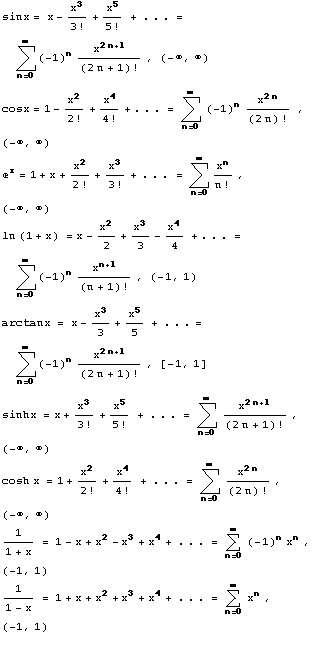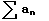
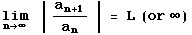 , the series
, the series
- converges absolutely if L < 1
- diverges if L > 1 or is infinite
Useful for factorials and nth powers.
For power series, let an be the entire power series term.
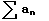
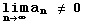
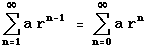
- Converges with sum
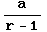 if |r|<1
if |r|<1 - Diverges otherwise
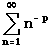
- Converges if p > 1
- Diverges otherwise
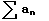
f(n) = an,
f(x) defined for x>1 is continuous, positive, and decreasing
(check f'(x) )
- Converges if
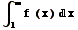 converges
converges - Diverges otherwise
 given,
given,
usually
 is chosen,
is chosen,
all terms in both series strictly positive
- If
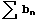 converges and an <= bn for every n,
then
converges and an <= bn for every n,
then 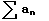 converges
converges - If
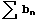 diverges and an >= bn for every n,
then
diverges and an >= bn for every n,
then 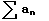 diverges
diverges
Often the b-series is geometric or a p-series. Consider terms of the a-series of greatest effect.
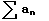 given,
given,
usually
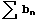 is chosen,
is chosen,
all terms in both series strictly positive
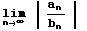 is finite then both series converge or both diverge.
is finite then both series converge or both diverge.
Often the b-series is geometric or a p-series. Consider terms of the a-series of greatest effect.
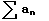
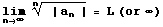 , the series
, the series
- converges absolutely if L < 1
- diverges if L > 1 or is infinite
Useful for nth powers, such as in power series.
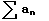
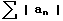 , then
, then
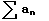 converges
converges
Useful for series with both positive and negative terms.
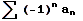 ,
an > 0
,
an > 0
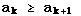 for every k and
for every k and
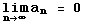
Note that an is the non-alternating part!
If inequalities are not easy, let f(n) = an.
f(x) defined for x>1 should be continuous, positive, and decreasing
(check f'(x) )